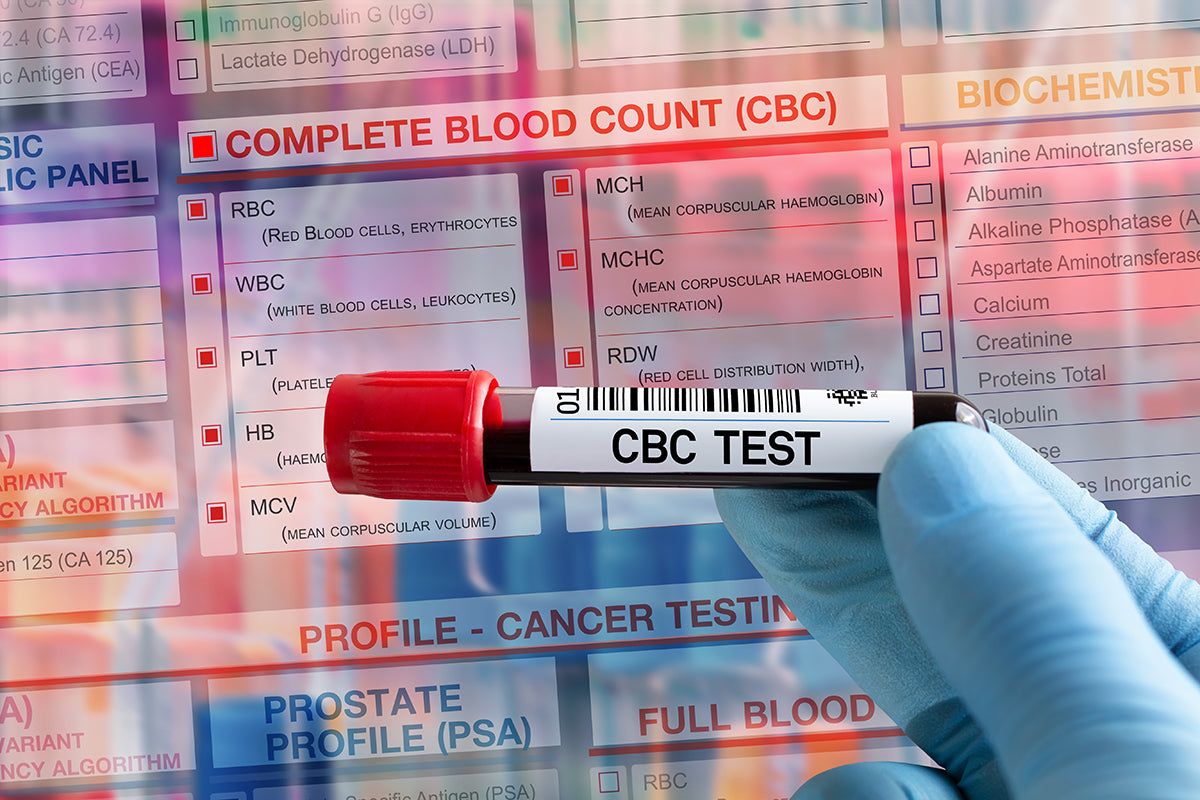
Complete blood count: number and size of all blood cells
|
|
Time to read 3 min
|
|
Time to read 3 min
A complete blood count is a set of medical laboratory tests performed on a blood sample to gather information about the number and functionality of blood cells.
The complete blood count encompasses the following tests:
Additional, less common tests that may be included are, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, reticulocyte count, blood smears for microscopic examination.
The complete blood count provides a comprehensive view of blood cell health.
Complete blood count results should fall within specific reference ranges. Deviations from these ranges can be concerning.
The complete blood count is used to detect various diseases, such as anemia, infections, and allergies, among others. The specific conditions detected depend on which parameters are abnormal.
The complete blood count test involves the simultaneous analysis of all included parameters.
Elevated red blood cell count, hemoglobin, or hematocrit, may be caused by:
Low red blood cell count, hemoglobin, or hematocrit, this indicates anemia, which may result from:
A white blood cell count below normal is referred to as leukopenia. This reduction may be caused by:
A high white blood cell count is called leukocytosis. It can result from:
A high platelet count may result from:
A low platelet count may result from:
The complete blood count is a set of medical laboratory tests performed from a blood sample in order to obtain information about the number of blood cells and their functionality.
The complete blood count results must remain within specific ranges. Any deviation from them is cause for concern.
The complete blood count test is performed through the simultaneous analysis of the determinations that include it.
Anemias, certain types of cancer and liver diseases are some of the different alterations that can be detected with the blood count.